You might be wondering why you paying more for your energy?
Simple answer: The energy price cap increased. On the first of April this year the energy price cap increased by 54%. What is a price cap?

Energy Financial Support
Households that are struggling with their energy use and costs should know that there is help and financial support available.
Across the United Kingdom, there are numerous sources of support to overcome fuel poverty or its related issues. If you would like to know more about what constitutes “fuel poverty”, a lookthrough our previous article “What is Fuel Poverty and how can it be alleviated?” might prove quite helpful.
Warm Home Discount Scheme
The Warm Home Discount Scheme (WHD) is funded by the energy suppliers. It provides direct and indirect financial support to vulnerable energy consumers.
The WHD scheme separates eligible households into two groups – the ‘Core’ group and the ‘Broader’ group.
Support under the Core Group is targeted at older, poorer pensioner households. A householder qualifies for the Core Group discount if on a specific day (to be confirmed) all of the following apply:
- their supplier was part of the scheme.
- their name (or their partner’s) was on the statement on a specified day in July.
- they were getting the Guarantee Credit element of Pension Credit (even if they get Savings Credit as well).
- Discount is £140.
Households who feel they may qualify for the WHD under their supplier’s Broader Group should submit an application directly to their supplier. Each company has its own set of qualifying conditions.
A link to the individual suppliers’ websites and their qualifying criteria can be found at: www.gov.uk/the-warm-home-discount-scheme/eligibility.

Trusts and Grants
Most of the energy suppliers offer a range of grants for their most vulnerable customers (subject to meeting certain criteria).
- British Gas (British Gas Energy Trust) – Payments for household bills/ energy arrears.
- EDF Energy (EDF Energy Customer Support Fund) – Payments for household bills/ energy arrears or essential appliances.
- E.ON (Energy Fund) – Will provide payments for household bills/ energy arrears, essential appliances and repairs to or replacement boilers.
- npower (Energy Fund) – Provides financial assistance to individuals and organisations.
- SSE Priority Assistance Fund – supports those who in or at risk of fuel poverty. Website includes information on support services.
- ScottishPower Hardship Fund – Provides help to customers having difficulty paying their bills due to low income. Electricity and gas arrears can be cleared or reduced by a credit from the fund to the customer’s account.
- Let’s Talk Energy Fund – Open to everybody regardless of energy supplier. It offers debt relief, boilers and white goods.
- Charis Grants – facilitates charitable and corporate giving by designing, developing and managing a range of services in support of vulnerable members of society. Website: www.charisgrants.com/
- Priority Services Register (PSR) – The Priority Services Register is a free service provided by fuel suppliers and network operators for vulnerable customers. Each energy supplier and network operator maintains its own register and will need you to contact them directly.
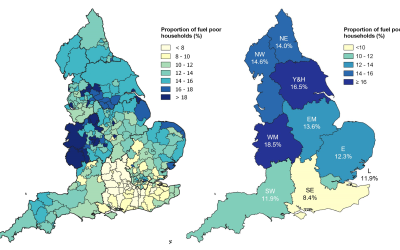
West Midlands has highest rates of fuel poverty in England
Changes announced to energy support packages
You might be wondering why you paying more for your energy?
Simple answer: The energy price cap increased. On the first of April this year the energy price cap increased by 54%. What is a price cap?
Government Support for Household Energy Bills
What does Government offer to help with rising energy costs?






Recent Comments